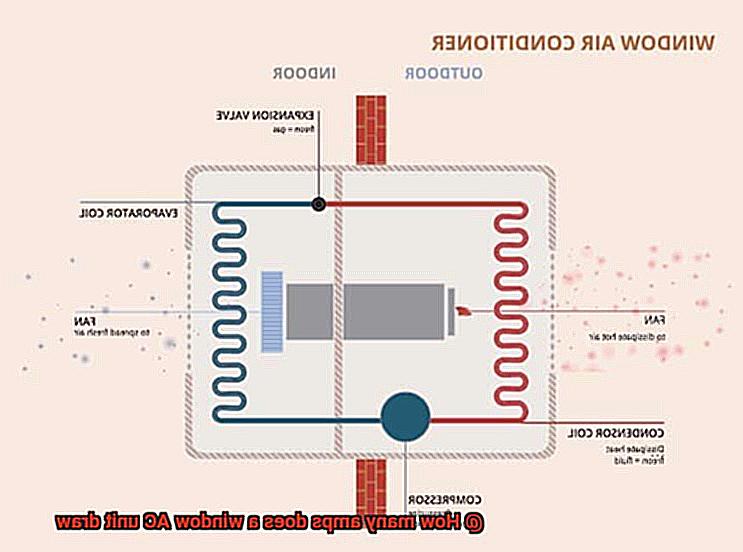
Are you tired of sweating through the summer months? Window AC units are a popular and affordable solution to keep your home cool and comfortable. But have you ever wondered how many amps a window AC unit draws, and why it matters?
Don’t worry, we’ve got you covered. The answer isn’t as simple as you might think. Factors such as the size of your unit, its cooling capacity, and energy efficiency rating all play a role in determining how much electricity it uses.
Knowing how many amps your AC unit draws is important because it can affect your energy bills and electrical performance. In this article, we’ll dive into the nitty-gritty details of how window AC units work, what affects their electricity consumption, and how to accurately calculate their amps rating.

Whether you’re a curious homeowner or just want to save some money on your energy bill, this article will help debunk common myths and demystify the world of window AC units. So sit back, relax, and get ready to become an expert on all things related to window AC units.
Factors That Affect the Amps Drawn by a Window AC Unit
Contents
- 1 Factors That Affect the Amps Drawn by a Window AC Unit
- 2 Calculating the Amps Drawn by a Window AC Unit
- 3 Other Factors to Consider When Shopping for an AC Unit
- 4 Benefits of Proper Maintenance of an AC Unit
- 5 Tips for Choosing an Energy-Efficient Window AC Unit
- 6 Common Mistakes to Avoid When Installing and Operating a Window AC Unit
- 7 Conclusion
Understanding the factors that affect the amps drawn by your AC unit can help you make informed decisions about energy efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Let’s dive into the factors that affect how much power your window AC unit consumes.
Firstly, the size of your unit plays a significant role. The larger the unit, the more amps it will consume. This is because larger units require more power to cool a larger space. So, if you have a small room to cool, consider choosing a smaller unit to save on electricity bills.
Secondly, the age of the unit also affects power consumption. Older units tend to be less energy-efficient and consume more power, resulting in higher amps being drawn. Consider upgrading to a newer, more energy-efficient model if you have an older unit.
Thirdly, adjusting the temperature setting on your AC unit can be a gamechanger when it comes to saving money on electricity bills. The lower the temperature setting, the more power it will consume. Adjusting the temperature to a higher setting can be a simple way to save on electricity bills without compromising on comfort.
Fourthly, a dirty filter can restrict airflow and cause your AC unit to work harder, leading to higher amps being drawn. Make sure to clean or replace your filter regularly to ensure optimum airflow and energy efficiency.
Lastly, external factors such as ambient temperature and humidity levels can also impact how many amps your AC unit draws. If it’s hot and humid outside, your AC unit will have to work harder to cool your space, leading to higher power consumption.
Calculating the Amps Drawn by a Window AC Unit
Understanding the amps drawn by your unit can help you save on energy bills and prevent potential fire hazards. In this blog post, we will guide you through the simple steps to calculate the amps drawn by your window AC unit.
Firstly, determine the voltage and wattage of your window AC unit. While most window AC units operate on 120 volts, it’s always best to check the manufacturer’s specifications to be sure. The wattage of the unit can usually be found on the nameplate or in the owner’s manual.
Now that you have these values, you can easily calculate the amps drawn using a simple formula:
Amps = Watts/Volts
Let’s say your window AC unit has a wattage of 1,200 watts and operates on 120 volts. Using the formula above, we can calculate the amps drawn by the unit:
- Amps = 1,200/120
- Amps = 10
In this case, your window AC unit consumes 10 amps of current when it is operating at full capacity. However, keep in mind that this is just an estimate and actual amp draw may vary depending on factors such as the age and condition of the unit and any additional features such as a built-in heater or dehumidifier.
Before installing a window AC unit in your home or office, make sure your electrical system can handle the additional load. Most circuits are rated for 15 or 20 amps, so if you’re installing a larger unit or multiple units, you may need to upgrade your electrical system to avoid overloading your circuits and causing a potential fire hazard.
Other Factors to Consider When Shopping for an AC Unit
While amps are important, there are several other factors to consider before making your final decision. Let’s dive into what else you should keep in mind:
Energy Efficiency Rating
Don’t overlook the importance of an AC unit’s Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER). By choosing a unit with a high SEER rating, you can reduce energy consumption and lower your utility bills in the long run.
Size
Bigger isn’t always better – choosing an AC unit that is sized properly for the room you need to cool is crucial. A unit that is too small will have to work harder, while one that is too large will cool the space too quickly and not properly dehumidify the air.
Refrigerant Type: Do your part to help protect the environment by choosing a unit that uses newer, more eco-friendly refrigerants. Some older refrigerants have been phased out due to their harmful effects on the environment.
Noise Level
If you plan on using your AC unit in a quiet space, such as a bedroom, noise level is an important factor to consider. Look for units with noise levels below 60 decibels to ensure a peaceful environment.
Benefits of Proper Maintenance of an AC Unit
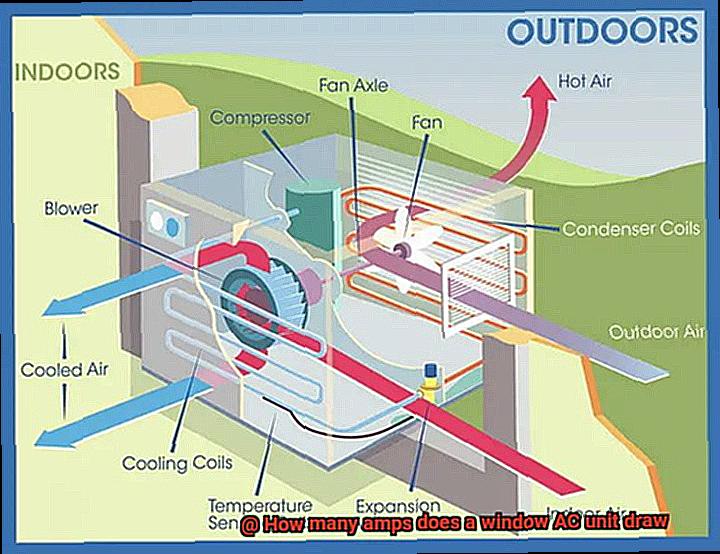
Not only does it help you save energy and money, but it also provides a healthier and more comfortable living or working environment.
Firstly, let’s talk about energy efficiency. Neglecting your AC unit’s maintenance can lead to higher energy consumption and costs as it struggles to cool down your space. By regularly cleaning and maintaining your unit, you can ensure that it operates at its optimal level without wasting energy or driving up your electricity bills.
But proper maintenance doesn’t just save you money – it also improves air quality. A dirty AC unit can circulate dust, dirt, and other allergens throughout a space, which can cause health problems for the occupants. Regular cleaning and replacing air filters can improve air quality and reduce the risk of respiratory issues, making your space a healthier place to be.
Moreover, maintaining your AC unit extends its lifespan. Just like any other mechanical device, wear and tear on the components can cause malfunctions and breakdowns if not properly maintained. Regular cleaning and upkeep will prevent this wear and tear, ensuring that your AC unit functions properly for years to come. This saves you money by avoiding costly repairs or replacements down the line.
Lastly, proper maintenance ensures a comfortable living or working environment. A well-maintained AC unit provides consistent cooling without any disruptions or malfunctions, guaranteeing that individuals are comfortable and productive. Imagine trying to work in a hot and stuffy office without proper AC maintenance – not fun.
Tips for Choosing an Energy-Efficient Window AC Unit
With so many options on the market, it can be overwhelming to choose the right one. That’s why we’ve compiled a list of tips to help you make an informed decision. Here are five factors to consider when selecting an energy-efficient window AC unit.
The Importance of Amperage in Choosing an Energy-Efficient Window AC Unit
When shopping for a window AC unit, pay attention to its amperage rating. Amperage refers to the amount of electrical current the unit draws, and the higher the amperage, the more energy it will consume. To choose an energy-efficient window AC unit, look for one with a low amperage rating. Typically, a 5,000 BTU unit will draw around 4 to 6 amps, while a 12,000 BTU unit may draw anywhere from 9 to 12 amps.

The Benefits of Choosing an Energy Star Rated Window AC Unit
Another factor to consider when choosing an energy-efficient window AC unit is its Energy Star rating. This program, run by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, identifies and promotes energy-efficient products. Energy Star-rated AC units are designed to use less energy than standard models while still providing reliable performance. By choosing an Energy Star-rated unit, you’ll not only save money on your electricity bill but also contribute to a greener planet.
Choosing the Right Size and Cooling Capacity
Selecting the right size and cooling capacity is crucial in ensuring that your window AC unit is both effective and efficient. A unit that is too large will waste energy and money, while a unit that is too small will struggle to cool the room effectively. To determine the appropriate size, measure the square footage of your space and consult with a professional or refer to manufacturer guidelines. Additionally, pay attention to the unit’s cooling capacity, which is measured in BTUs. A higher BTU rating means a more powerful cooling capacity, but it also means higher energy consumption, so aim for a balance between cooling power and energy efficiency.
Features to Look for in an Energy-Efficient Window AC Unit
There are several features to look for when choosing an energy-efficient window AC unit. Programmable thermostats allow you to set a schedule for when the unit should turn on and off, reducing unnecessary cooling and saving energy. Units with variable-speed fans are more efficient than those with fixed-speed fans, as they allow you to adjust the fan speed based on your cooling needs. Finally, units with high-efficiency compressors and coils can cool your space more efficiently and save even more energy.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Installing and Operating a Window AC Unit
Before you start, it’s important to know the common mistakes people make when installing and operating these units. Avoiding these mistakes will ensure optimal performance and efficiency, while keeping your energy costs low and your home cool and comfortable.
One of the most significant mistakes is not considering the electrical requirements of the unit. To avoid any electrical mishaps, be sure to check how many amps the unit draws before installation. Smaller units draw around five to seven amps, while larger ones can draw up to 15 amps or more. Knowing this information will ensure that your electrical system can handle the load.
Another mistake is not properly sealing the unit in the window. When there are air leaks around the unit, it decreases efficiency and increases energy costs. So don’t forget to seal all gaps around the unit using weatherstripping or foam insulation.
Setting the thermostat too low or too high is another common mistake people make. If it’s too low, it will cause the unit to work harder than necessary, leading to increased energy costs and decreased performance. If it’s too high, it won’t provide adequate cooling for your home. So, set your thermostat at an optimal temperature for your comfort and your unit’s efficiency.
Finally, regular maintenance is crucial for optimal performance and safety. Neglecting maintenance can lead to decreased performance and even safety hazards. Be sure to clean or replace the filter regularly and inspect the unit for any signs of wear or damage.
DjHTK2V_yD4″ >
Conclusion
In conclusion, when it comes to keeping your home cool and comfortable during the hot summer months, a window AC unit is a popular and affordable solution. However, it’s essential to understand how many amps your unit draws as this can significantly impact your energy bills and electrical performance.
Factors such as the size of your unit, its cooling capacity, and energy efficiency rating all play a crucial role in determining how much electricity it uses. To accurately calculate the amps drawn by your window AC unit, you need to determine its voltage and wattage. Armed with this information, you can use a simple formula to calculate the amps drawn by the unit.
But that’s not all. When shopping for an energy-efficient window AC unit, there are other factors to consider besides just amps drawn. Energy Star ratings, size, cooling capacity, programmable thermostats and variable-speed fans are all essential features that can help you save money on energy bills while enjoying a comfortable living environment.
Regular maintenance of your AC unit is also crucial for optimal performance and safety. Neglecting maintenance can lead to decreased performance or even safety hazards. So make sure you clean or replace filters regularly and inspect the unit for any signs of wear or damage.
You may also like: